WNC Orchard Insect Populations – May 14, 2019
go.ncsu.edu/readext?602537
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
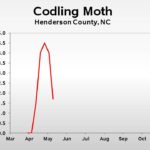
Collapse ▲ Codling Moth: We remain in the timeframe when codling moth is the key insect of concern in apples. Degree-day accumulations since biofix range from about 360 in Henderson County (2100 ft elevation) to about 550 in Cleveland County (850 ft). First generation codling moth can remain active through about 600 to 800 DD, depending on population density. Generally, the higher the population the later activity declines.
Codling Moth: We remain in the timeframe when codling moth is the key insect of concern in apples. Degree-day accumulations since biofix range from about 360 in Henderson County (2100 ft elevation) to about 550 in Cleveland County (850 ft). First generation codling moth can remain active through about 600 to 800 DD, depending on population density. Generally, the higher the population the later activity declines.
In locations of about 2000 ft elevation, 350 DD coincides with the optimum timing for the first of either one or two applications against the first generation. A second application is recommended in another two to three weeks, at which time a spray for tufted apple bud moth is also recommended.
In lower elevations, where DD accumulations average about 550, a final spray for first generation codling moth in orchards with low to moderate populations is recommended at this time. This will also coincide with tufted apple bud moth (TABM) in these locations.
It should be noted that the above are general recommendations for orchards that are not using mating disruption. The number of sprays required will vary depending on the intensity of populations, and the only way to know population intensity is with the use of pheromone traps (See the article from April 10 on pheromone trapping). In some instances only one insecticide spray will be necessary, while in orchards with high populations as many as 3 or 4 applications may be necessary.
As in past years, Altacor and Delegate remain the most effective insecticides against codling moth, and whichever product is used against the first generation should NOT be used against the second generation in July – it is necessary to alternate insecticides against generations. Also, for those orchards with very low codling moth populations and where only one application may be necessary, you may want to consider Intrepid for a second application where TABM control is also necessary, Intrepid is an excellent product for control of TABM, but should not be relied upon for control of moderate to high codling moth populations.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug: Much of the BMSB population has emerged from overwintering sites, and emergence is expected to be complete in the next week or two. To date populations have been relatively low, averaging less than one per trap across the region. Beginning next week we will provide degree-day accumulations for BMSB and estimates of when first generation adult emergence is expected. While things can always change, at this time we do not expect action will be necessary against this pest until July (Piedmont) or August (mountains).
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2019 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 29 |
May 6 |
May 13 |
|
| Codling Moth | 4.5 | 4.0 | 1.7 |
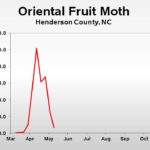
| Oriental Fruit Moth | 67.5 | 26.3 | 6.7 |
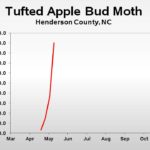
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | 15.0 | 37.0 | 90.0 |
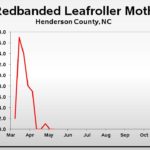
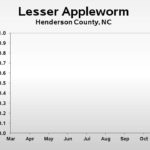
| Redbanded Leafroller | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
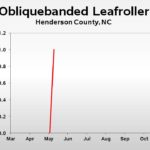
| Obliquebanded Leafroller | – | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Lesser Appleworm | – | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Apple Maggot (abandoned and research) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – mountains) | 1.4 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – upper Piedmont) | 3.7 | 3.3 | 1.7 |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (research – unsprayed) | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
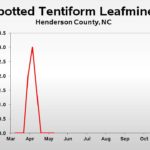
| Spotted Tentiform Leafminer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
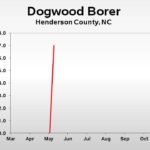
| Dogwood Borer | – | 0.0 | 7.0 |
| Peachtree Borer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
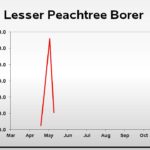
| Lesser Peachtree Borer | 58.0 | 112.0 | 21.0 |
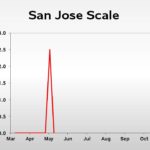
| San Jose Scale | 0.0 | 2.5 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2019 Accumulated Degree Days
| Henderson County | ||||
| Biofix | Apr 29 |
May 7 |
May 14 |
|
| Codling Moth | Apr 15 | 133 | 260 | 377 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | Mar 16 | 466 | 632 | 760 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | Apr 20 | 124 | 290 | 417 |
2019 Pest Trends (click to enlarge)
PREVIOUS UPDATES
May 7, 2019
 Codling Moth: The major insect of concern at this time is the codling moth. Degree-day accumulation in the mountains at about 2100 ft elevation was 260 as of May 6, and in the piedmont at an elevation of 900 ft, it was 400.
Codling Moth: The major insect of concern at this time is the codling moth. Degree-day accumulation in the mountains at about 2100 ft elevation was 260 as of May 6, and in the piedmont at an elevation of 900 ft, it was 400.
In orchards with moderate to high populations of codling moth, first generation egg hatch begins at about 250 DD, so in those orchards an insecticide effective against codling moth should already have been made. In orchards with low populations – i.e., none or very low damage last year and no more than about 2 moths captured in pheromone traps during the past week – waiting until about 350 DD for an initial application is most efficient. In the mountains this is predicted to occur early next week, and in piedmont orchards we are beyond that point.
Remember, the above predictions are for orchards NOT using mating disruption. Where mating disruption is being used for codling moth and OFM, an insecticide is not recommended until tufted apple bud moth cumulative degree days reach 600 to 800.
European Red Mite Sighting: There have been reports of European red mite showing up on apples this week in Henderson County. In the past 20 years, this is only the second time I am aware of ERM appearing this early in the season. This is unusually early, and probably reflects the more widespread use of pyrethroids in recent years. Hence, in those orchards that did not use a preventive miticide application (e.g., Agri-Mek, Zeal, Apollo, Savey or Envidor), it would be wise to check your most mite-susceptible blocks.
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2019 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 22 |
Apr 29 |
May 6 |
|
| Codling Moth | 4.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | 61.0 | 67.5 | 26.3 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | 3.0 | 15.0 | 37.0 |
| Redbanded Leafroller | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Obliquebanded Leafroller | – | – | 0.0 |
| Lesser Appleworm | – | – | 0.0 |
| Apple Maggot (abandoned and research) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – mountains) | – | 1.4 | 1.0 |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – upper Piedmont) | – | 3.7 | 3.3 |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (research – unsprayed) | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Spotted Tentiform Leafminer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Dogwood Borer | – | – | 0.0 |
| Peachtree Borer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lesser Peachtree Borer | 5.0 | 58.0 | 112.0 |
| San Jose Scale | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2019 Accumulated Degree Days
| Henderson County | ||||
| Biofix | Apr 22 |
Apr 30 |
May 7 |
|
| Codling Moth | Apr 15 | 45 | 133 | 260 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | Mar 16 | 348 | 466 | 632 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | Apr 20 | 18 | 124 | 290 |
April 30, 2019
By now petal fall applications have been made in most locations except for the highest elevation orchards (e.g., ≥3000 feet), and attention can now move to other pests – especially the codling moth.
Codling Moth: Codling moth biofix date in Henderson County (elevation about 2100 ft) occurred on 15 April. Typically biofix occurs about a week earlier off the mountain in Cleveland and Lincoln Counties (about 900ft), and is estimated to have occurred on 8 April. Codling moth egg hatch begins at about 250 cumulative degree days (DD), which is the recommended timing of first insecticide applications in orchards with moderate to high populations. For orchards with low populations, which is the more common situation, the initial timing can be delayed to about 350 DD.
In Henderson County we are currently at about 133 DD, and 250 DD is estimated to occur next Monday (May 6) and 350 DD on May 11. Off the mountain at an elevation of about 900 ft (Cleveland/Lincoln County), we are currently at about 300 DD and 350 is predicted for later this week on Friday or Saturday (May 3 or 4).
In orchards using mating disruption and where pheromone trap captures remain low, insecticides for codling moth are not necessary at this time. In most situations with mating disruption a single insecticide application against the first generation codling moth is not recommended until about 600-700 DD have accumulated, which coincides with the optimum timing of first generation tufted apple bud moth (TABM).
Regarding insecticides recommended for codling moth, they remain Altacor (3 oz/A) and Delegate (6 oz/A). One product should be used for all first-generation applications, and the other product against the second generation in July.
San Jose Scale: For those that are concerned about San Jose scale and have not yet applied an insecticide effective against this pest, anytime within the next two weeks is ideal timing for application of either Esteem or Centaur, both of which provide excellent control when used at this time.
Another option is use of Movento, which can also provide suppression of woolly apple aphid (WAA) later in the season. The systemic activity of Movento, which is unique in that it moves in both directions in the tree (leaf to leaf, and leaf to roots), is key to preventive control of WAA. It should be noted, however, that WAA is a sporadic pest and often does not develop to pest status. If using Movento, it is important to read the label to ensure proper use. It must be used with an adjuvant with spreading and penetrating properties to maximize leaf uptake for systemic activity. However, DO NOT use Induce, due to compatibility issues.
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2019 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 15 |
Apr 22 |
Apr 29 |
|
| Codling Moth | 1.5 | 4.0 | 4.5 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | 101.5 | 61.0 | 67.5 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | – | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Redbanded Leafroller | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Obliquebanded Leafroller | – | – | – |
| Lesser Appleworm | – | – | – |
| Apple Maggot (abandoned and research) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – mountains) | – | – | 1.4 |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – upper Piedmont) | – | – | 3.7 |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (research – unsprayed) | 0.2 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Spotted Tentiform Leafminer | n/a | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Dogwood Borer | – | – | – |
| Peachtree Borer | – | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lesser Peachtree Borer | – | 5.0 | 58.0 |
| San Jose Scale | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2019 Accumulated Degree Days
| Henderson County | ||||
| Biofix | Apr 15 |
Apr 22 |
Apr 30 |
|
| Codling Moth | Apr 15 | – | 45 | 133 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | Mar 16 | 282 | 348 | 466 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | Apr 20 | – | 18 | 124 |
April 23, 2019
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2019 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 8 | Apr 15 |
Apr 22 |
|
| Codling Moth | 0.0 | 1.5 | 4.0 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | 55.0 | 101.5 | 61.0 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | – | – | 3.0 |
| Redbanded Leafroller | 7.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Obliquebanded Leafroller | – | – | – |
| Lesser Appleworm | – | – | – |
| Apple Maggot (abandoned and research) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – mountains) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – upper Piedmont) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (research – unsprayed) | – | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Spotted Tentiform Leafminer | 3.0 | n/a | 0.0 |
| Dogwood Borer | – | – | – |
| Peachtree Borer | – | – | 0.0 |
| Lesser Peachtree Borer | – | – | 5.0 |
| San Jose Scale | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2019 Accumulated Degree Days
| Henderson County | ||||
| Biofix | Apr 7 |
Apr 15 |
Apr 23 |
|
| Codling Moth | Apr 15 | – | – | 45 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | Mar 16 | 151 | 282 | 348 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | – | – | – | – |
April 16, 2019
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2019 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 1 | Apr 8 |
Apr 15 |
|
| Codling Moth | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | 1.0 | 55.0 | 101.5 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | – | – | – |
| Redbanded Leafroller | 17.0 | 7.0 | 0.0 |
| Obliquebanded Leafroller | – | – | – |
| Lesser Appleworm | – | – | – |
| Apple Maggot (abandoned and research) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – mountains) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – upper Piedmont) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (research – unsprayed) | – | – | 0.2 |
| Spotted Tentiform Leafminer | 2.0 | 3.0 | n/a |
| Dogwood Borer | – | – | – |
| Peachtree Borer | – | – | – |
| Lesser Peachtree Borer | – | – | – |
| San Jose Scale | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2019 Accumulated Degree Days
| Henderson County | ||||
| Biofix | Apr 1 |
Apr 7 |
Apr 15 |
|
| Codling Moth | – | – | – | – |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | Mar 16 | 87 | 151 | 281.5 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | – | – | – | – |
April 8, 2019
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2019 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Mar 25 | Apr 1 | Apr 8 |
|
| Codling Moth | set | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | 1.0 | 1.0 | 55.0 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | – | – | – |
| Redbanded Leafroller | 14.0 | 17.0 | 7.0 |
| Obliquebanded Leafroller | – | – | – |
| Lesser Appleworm | – | – | – |
| Apple Maggot (abandoned and research) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – mountains) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (commercial – upper Piedmont) | – | – | – |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (research – unsprayed) | – | – | |
| Spotted Tentiform Leafminer | 0.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| Dogwood Borer | – | – | |
| Peachtree Borer | – | – | |
| Lesser Peachtree Borer | – | – | |
| San Jose Scale | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2019 Accumulated Degree Days
| Henderson County | ||||
| Biofix | Mar 25 | Apr 1 | Apr 7 |
|
| Codling Moth | – | – | – | – |
| Oriental Fruit Moth | Mar 16 | 41 | 87 | 151 |
| Tufted Apple Bud Moth | – | – | – | – |