Apple Disease Update: Week of June 7, 2021
go.ncsu.edu/readext?802456
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲In this week’s post, I’d like to address a question that has been popping up recently: Options for flyspeck/sooty blotch (FSSB) management? In a separate post this week (likely to be published tomorrow, June 9) I also plan on addressing another question that has come through my email a few times: The importance of adding ProPhyt (or another phos. acid fungicide) to captan for summer disease management.
Management for FSSB
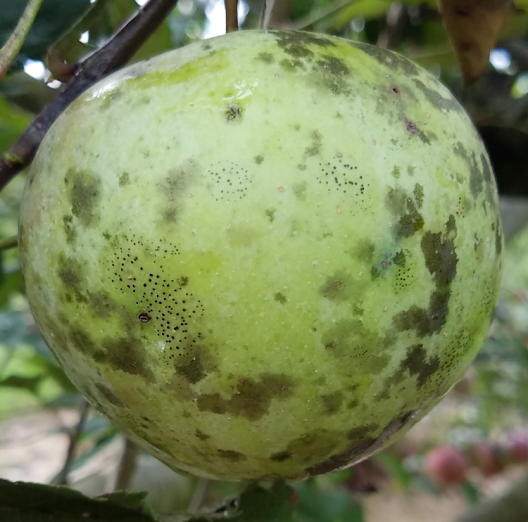
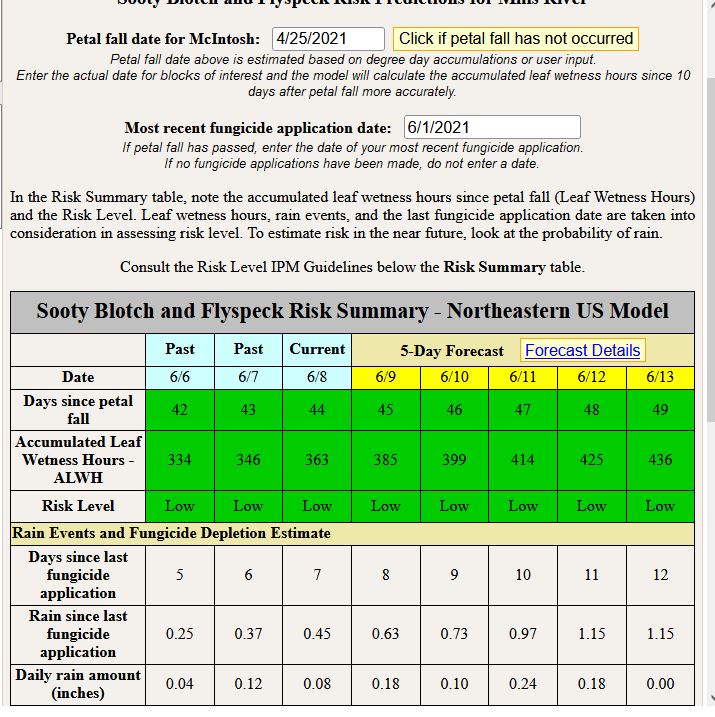
Flyspeck and sooty blotch are considered a cosmetic disease of apple and unless infections are highly severe, processing growers should not invest too many resources into managing this disease. Caused by several different fungal species, for fresh market producers, management for FSSB should commence during the early cover applications and continue through harvest. Fortunately, management is a breeze compared to bitter rot. An FSSB model which takes into account leaf wetting hours past the date of petal fall and general fungicide residue depletion is available through the NEWA disease forecasting system (newa.cornell.edu). 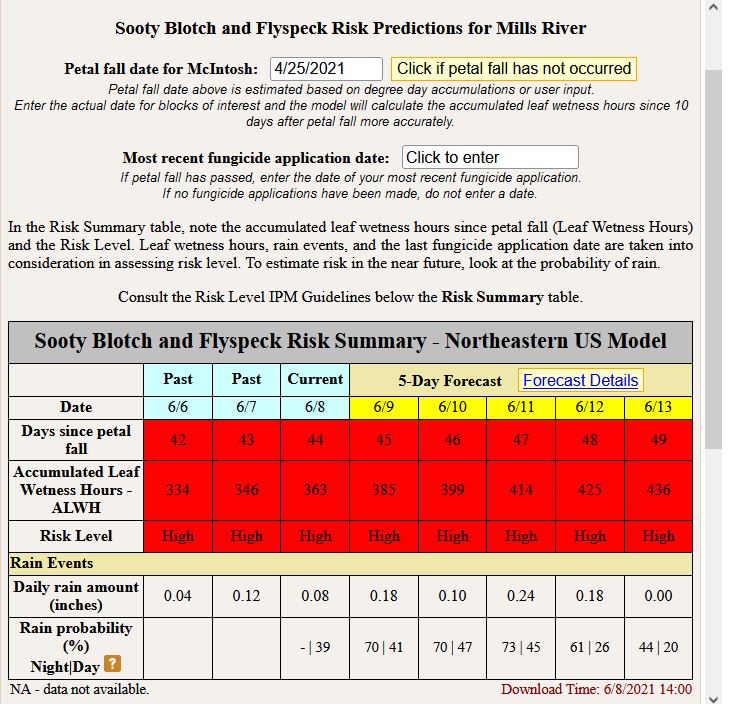 Above is the risk of infection by FSSB pathogens at the MHCREC in Mills River for Tuesday, June 8. Notice there are only two sections for input: Date of petal fall on McIntosh and date of last fungicide application. Since we don’t grow many Macs down here, I suggest entering the date of “Gala’ petal in your orchard. In the above scenario I chose not to enter a fungicide application for comparison purposes later. Note the model tracks accumulated leaf wetness hours and days since petal fall. After a FSSB fungal spores lands on a fruit surface, it takes approx. 273 hours for symptoms of the disease to begin to show. Given the high humidity often experienced in Western NC, accumulated wetting hours are not difficult to achieve.
Above is the risk of infection by FSSB pathogens at the MHCREC in Mills River for Tuesday, June 8. Notice there are only two sections for input: Date of petal fall on McIntosh and date of last fungicide application. Since we don’t grow many Macs down here, I suggest entering the date of “Gala’ petal in your orchard. In the above scenario I chose not to enter a fungicide application for comparison purposes later. Note the model tracks accumulated leaf wetness hours and days since petal fall. After a FSSB fungal spores lands on a fruit surface, it takes approx. 273 hours for symptoms of the disease to begin to show. Given the high humidity often experienced in Western NC, accumulated wetting hours are not difficult to achieve.
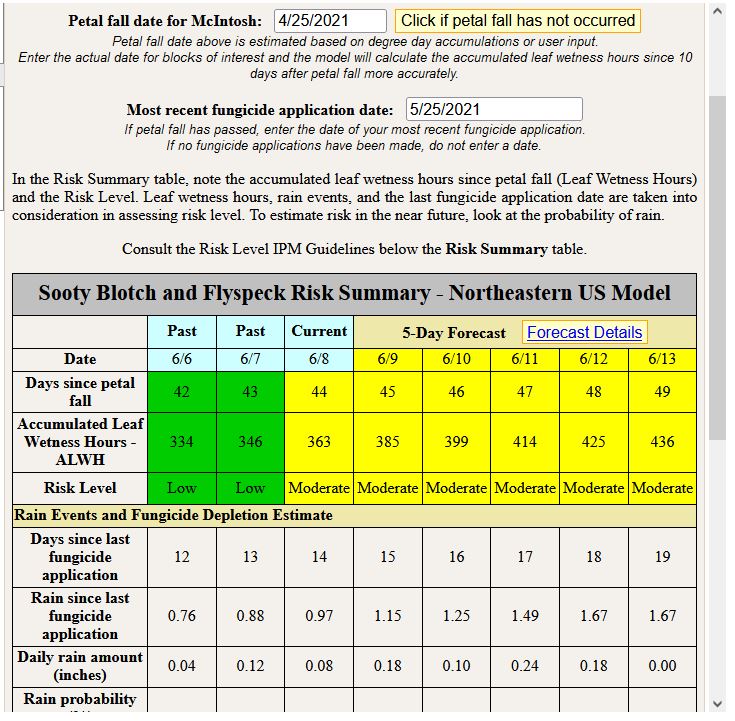
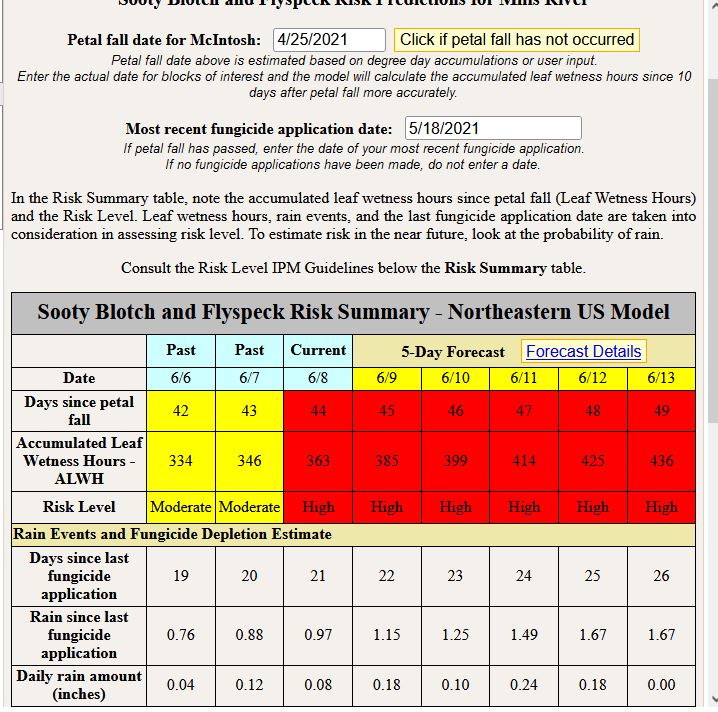
Once the 273 accumulated leaf wetness hours are achieved, management of FSSB becomes a fungicide residue game. Unfortunately, this model does not take into account for specific fungicides so it’s important to keep in mind that fungicides such as captan or ziram or T-Methyl (e.g. Topsin) will break down faster than fungicides such as Flint, Merivon, or Inspire Super and will thus require more frequent applications. It certainly depends on rain amount, but I would be hesitant to extend my application schedule to greater than 14 days for FSSB management, especially if a fungicide with shorter half life (faster break down) is applied. Below, are three scenarios: In the first scenario the model shows FSSB risk when fungicides were applied 7 days ago, the second scenario 14 days ago, and the 3rd scenario 21 days ago:
In regards to what to spray for FSSB control, we’ve generally had decent control against the disease with captan covers applied every 7-10 days at 3/4 of full rate. From my understanding, several growers throughout the region have not had the same fortune as we have had at MHCREC with this approach-this could be due to different pathogens causing FSSB symptoms or different application intervals.
In addition to evaluating the efficacy of summer fungicide programs (petal fall to harvest) against GLS and bitter rot, we also take harvest data on flyspeck and sooty blotch incidence (see graph below). Fungicide applications commenced at 50% petal fall and continued on 7 to 10-day intervals until harvest on 21-yr-old ‘Tenroy Gala’ grafted to M7 rootstock. All programs were “non-rotational” meaning that within a treatment, the same fungicide was applied throughout the entire season. No, this is not considered a legal commercial program, but we wanted a direct comparison across different fungicide groups.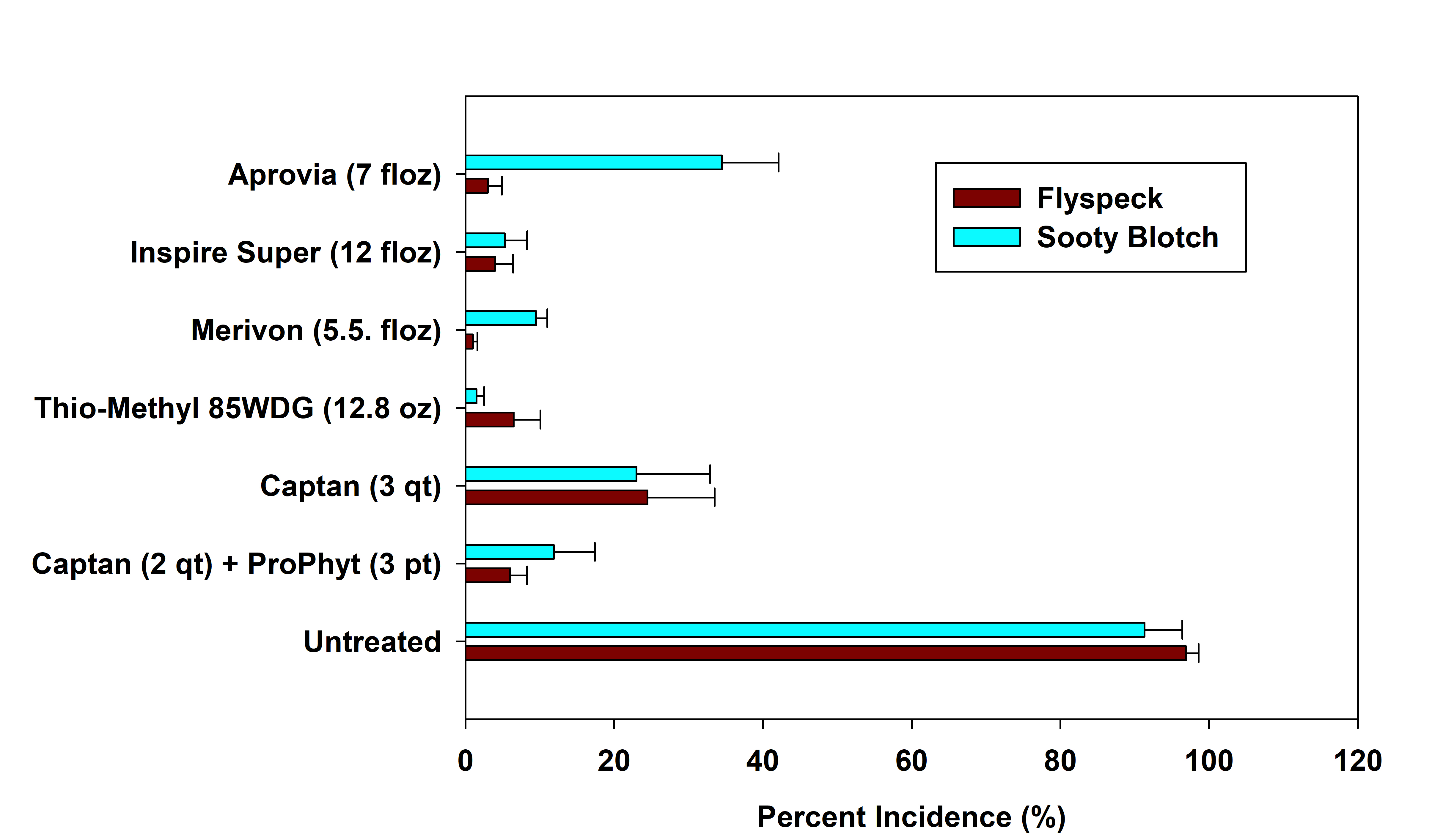
As you can see from the untreated program, there was high disease pressure as greater than 90% incidence was observed for both flyspeck and sooty blotch (FSSB) Including ProPhyt with captan reduced the incidence of flyspeck and significantly reduced the incidence of sooty blotch compared to captan applied alone. Incorporating a DMI fungicide such as Inspire Super or thiophanate-methyl (e.g. Topsin) provided the greatest control against FSSB, whereas other fungicides containing active ingredients in other FRAC groups (e.g., Aprovia, Merivon) tended to reduce the incidence of flyspeck to a much greater extent than sooty blotch.
What Fungicides to spray this Week?
If Merivon or another FRAC 11 fungicide was not applied either of your last two sprays, you may want to consider including it in a tank mix with Captan (half rate) as rain, high humidity, and warm temps are in the forecast. If you have applied Merivon recently, consider an application of Captan (3/4 rate), Captan (1/2-3/4 rate) + 3-4 pts ProPhyt, Captan (1/2 rate) + Ziram (1/2 rate) or Captan (1/2 rate) + a FSSB fungicide with good efficacy (see above) if you have only been applying captan over the past two weeks. Make sure to keep intervals tight on cultivars that are highly susceptible to bitter rot/Glomerella leaf spot (no more than 10 days).